Banking & Compliance Post Pandemic
A World of Change
Traditional banking and the wind of change are not inherently linked, but now more than ever, it seems that the change offered by modern technology is not only adopted, but due to the pandemic is happening at an accelerated pace. From the demand for more speedy processes, through the increased trend of closing branches, and all the way to new possibilities that the digital arena offers (including AI and Machine Learning). All this without even mentioning Crypto and the challenges it posts to traditional banks. Weather we like it or not, change is all around us. Here are some highlights from our recent webinar where we discussed banking and compliance post pandemic:
Increased Closing of Branches
Truth be told, the trend of closing branches has been apparent even before the pandemic. But as you can see from the image below, the pandemic has accelerated this trend:
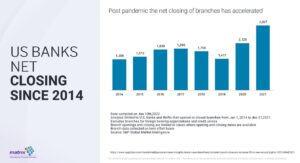
Approx. 3000 branches have been closed during 2021, and this has been taking place all over the US. Some of the reasons are tough operating environments and some have to do with the fact that traditional banks are now adopting to digital & innovative tools.
Innovative Tools
New technologies are coming in to play, and one of those is facial biometrics. Although there is a lot less face to face, the verification still needs to happen. This powerful tool was previously mainly for early adopters, but is becoming more mainstream.

Facial biometrics are much more likely to reduce risk and allow banks to ID and verify. It allows banks to explore card appliers and their relationships to other bad actors. This is all a part of the digital transformation that the banking industry is going through.
Digital Transformation
There are 3 ways to look at how this transformation is taking place:
- Digitisation – The process of making information available and accessible in a digital format
- Digitalisation – Use of Digital Technology and digital data to achieve set business process improvements – This is most banks are at. For example: depositing check s using your smartphones and improving the client’s experience.
- Digital Transformation – Using digital technologies to create new — or modify existing — business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet changing business and market requirements.
The 3rd option is banks want to be – to use technology to solve problems. For example:
Banks work in silos, and often a client would talk to a different teams when it comes onboarding, opening the account and applying for loans. The idea behind Digital Transformation is to break down barriers and consolidate the communication for the sake of better user experience. This is easier said than done, but some examples include the usage of AI and Blockchain.
2022 Trends
- Build Transparency with customers and open banking
- Data as predictable personalization tool
- AI providing more targeted services
- Increased Cloud Computing
- Increased automation
- Reliability is the key
- Security and Privacy
- Speed and Reactivity
In our Webinar we explored these trends more in depth, and further more we looked at 2 of the currently more prominent trends: Crypto & Neobanks
Virtual Currencies
Up until not so long ago FI’s were concerned of Virtual Asset activity on their platforms and not there weren’t many banking virtual asset service providers. What happened to trigger the change in approach? Well, 1st there was the OCC Custody Rule and FI’s couldn’t really ignore the market conditions and changes – Bitcoin valuation, Musk, Coinbase IPO and more.
Today however, virtual assets are mainstream, retail and institutional investors are rushing in and banks have to adapt to customers demanding to invest in Virtual Assets, and there is a change in the regulatory landscape from Enforcement to Support for New Business Strategy

The Rise of Neobanks
Neobanks, sometimes referred to as “challenger banks,” are fintech firms that offer apps, software and other technologies to streamline mobile and online banking. U.S. data suggest there are about 23 million Neobank customers. That number is expected to more than double, to 50 million, by 2025. Along with clear cut advantages such as leveraging new technologies and tech based agile approach, as well as less red tape and formalities than traditional banks, there are also disadvantages. In their bid to increase customer base and enable faster service processing, Neobanks are likely to undermine AML/CFT controls stipulated by watchdogs. Here are recent examples:
- German Neobank N26 has been fined €4.25m by the German financial services regulator for weak anti-money laundering practices.
- Digital bank Monzo is being investigated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) over potential breaches of financial crime regulations.
- Revolut’s compliance headaches regarding a whistleblower case which highlights AML concerns.
- Chime forced to ditch use of word ‘bank’ after regulator’s pushback.
For more information and in depth analysis of these new financial institutions, check our webinar, where we also discussed how to navigate AML between emerging risks and regulatory changes, as well as some solution updates regarding Screening, Sanctions and CDD.
Key Takeaways
Here are some (not all) of the key takeaways from our recent webinar on banking and compliance post pandemic:
- Don’t let your solutions get stagnant
- Regulatory uncertainty and changes is here to exist
- Pandemic has further accelerated digital adoption
- Robust Compliance Program can serve as a powerful FinCrime deterrent
Find out more
Please complete your details and we will contact you



Enter your contact details
Please submit your details
Enter your contact details
Please submit your details